Microbiological Testing For Nonsterile Dietary Supplements
What are non-sterile processes?
Non-sterile processes are methods or procedures undertaken in an environment where bioburden is controlled to safety levels based on product attributes, route of administration, and target patient population. Non-sterile processes contrast to sterile processes, in which the bioburden is essentially eliminated.
What are examples of common medical products manufactured in non-sterile environments?
- Metered-dose and dry powder inhalants
- Nasal sprays
- Optics
- Vaginal suppositories
- Topicals
- Rectal suppositories
- Oral liquids (aqueous)
- Liquid-filled capsules
- Oral tablets and powder-filled capsules
The non-sterile products listed above are ranked for potential risk of microbiological contamination (from high to low). The same list applies to medical devices for use in the same areas of the body (nasopharynx, vagina, skin, rectum, and mouth).
What are dietary supplements?
Dietary supplements are growing in popularity as bulk production of foods leads to nutritional deficiencies. Dietary supplements are being manufactured to supplement elements of our diets to combat these nutritional deficiencies. Examples of supplements include one or a combination of botanicals, amino acids, minerals, vitamins, and enzymes. Supplements come in multiple forms, including oral tablets, powders, encapsulated pills, and liquids.
Why is microbiological testing and monitoring important for dietary supplements?
Microbiological testing and monitoring are critical to keeping harmful bacteria, yeast, and molds out of supplement products. Products that don’t meet nonsterile microbial limits are dangerous and risk causing patient illness upon use. Microbial contaminants enter the manufacturing process in a variety of ways. The first and most common way is through the raw materials, pharmaceutical ingredients, and active ingredients used in nutritional and dietary supplement manufacture. Indeed, supplement components received from suppliers are not sterile. In particular, botanicals may be microbiologically contaminated with human or animal feces and molds at any point during growth, harvesting, processing, packing, or distribution. Thus, the level of microbiological contamination (bioburden) for a supplement’s raw ingredients must be monitored during manufacture. This monitoring prevents patient illness upon dietary supplement use. The second way microbial contaminants enter supplement products is during the manufacturing process. Microbial contaminants can enter manufactured products through facility environments (human operators & technicians), manufacturing equipment, and water use. Due to the contamination risks during manufacture, reliable dietary supplements are processed under Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) protocols. These GMP protocols control raw material bioburden, facility environments, equipment cleaning, water sources, and manufacturing process to minimize microbial content and contamination during product manufacture.

How is microbial monitoring of facilities, equipment, water, and supplement components for non-sterile products performed?
Facilities
Manufacturing facilities, including the building and the heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems, should be designed to limit microorganism contamination. Regular air samples are taken to ensure that cleanrooms and processing areas meet appropriate microbial limits. Further, facility temperatures, pressure differentials, and relative humidity levels are controlled to keep manufacturing environments cool and dry and prevent microbial growth.
Equipment
Equipment for processing semisolid and dry supplements control and eliminate microbial contaminants by being self-drying, easy to clean, and designed to promote product sanitation. Examples of equipment used for dietary supplements are dryers, ovens, wet granulation equipment, bulk tanks, and equipment for product coating solutions. These items are periodically evaluated to ensure cleaning and use procedures keep microbial contaminants at appropriate levels for non-sterile products.
Water
Water is a growth medium for a variety of microorganisms, especially molds and gram-negative bacteria. As a result, the water used in dietary supplement manufacturing and cleaning processes is purified water. The most problematic exposures to water during manufacturing are the use of purified water for wet granulation, batching liquid products, and film-coating tablets because water encourages microbial growth. Thus, GMP processes are required to minimize microorganism contamination during these activities. Additionally, cleaning and sanitation procedures must be developed and validated to ensure that any water used to clean manufacturing equipment and product contact surfaces doesn’t create unwanted microbial growth.
Supplement Components
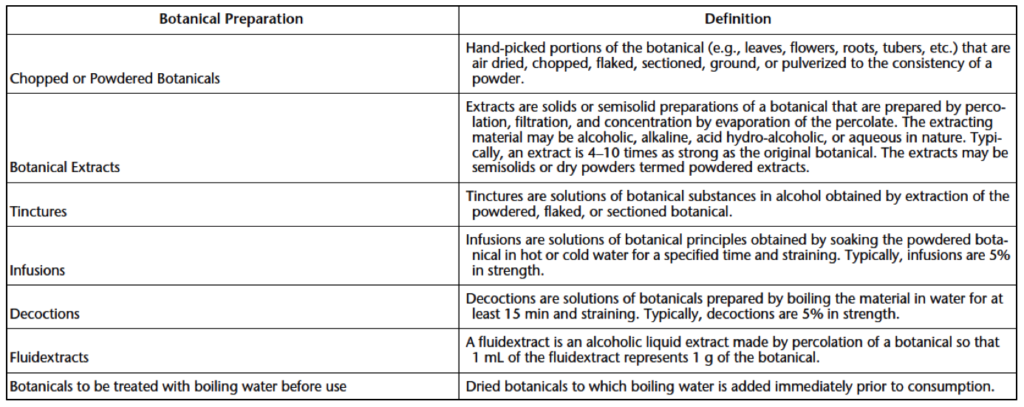
Raw materials, excipients, active supplements, and their suppliers must be evaluated to control the incoming bioburden of a manufactured product. Raw materials with high or unpredictable microbial levels (such as materials originating from animals or botanicals) require a pre-manufacturing process. Examples of pre-manufacturing processes include drying, extraction, heat treatment, irradiation, or gaseous sterilization to inactivate or remove microbial contaminants to a level safe for supplement manufacturing. If raw material pretreatment is necessary, ensure that the selected technique does not have any adverse effects on the activity or safety of the supplement ingredient. When it comes to fresh botanicals, bacteria are the predominant contaminant for new leaves. Yeast or fungi become dominant contaminants later in the growing season. With dried botanicals, the microorganism population will primarily be Gram-positive spore formers and fungi. Botanicals stored as powdered extracts using alcoholic, alkaline, acid hydro-alcoholic, or aqueous extracting materials have the lowest microbial content. Definitions for various botanical materials can be found in Table 1 below.
How frequently are microbiological tests performed?
Microbial enumerations tests include membrane filtration, plate, and multiple tube testing methods. These tests quantify the total aerobic microbial count (TAMC) and total combined yeasts and molds count (TYMC) in colony-forming units (CFU) for nonsterile supplements and their constituents.
In terms of microbial testing frequency, microbe sampling and testing plans vary based on the type of supplement and its route of administration. Examples of other products that need less routine microbial testing include highly refined botanical extracts and products with low water activity. In some cases, such as with dry oral dosage forms, little testing is necessary. In other cases, such as oral liquid dosage forms, periodic monitoring may be warranted.
Items to consider when designing microbial sampling and testing plans for supplements are:
- Route of administration of the supplement (oral, nasal, etc.)
- Microbial level of raw materials (dried herb vs. highly refined botanical extract)
- Product type (tablet, powder, pill, liquid, etc.)
- Method of manufacture and the potential for contamination during processing
- Growth promotion or inhibition properties of the supplement formulation (such as water content)
- The target population for the supplement
- Batch-to-batch supplement variability
What are the accepted microbial limits for non-sterile dietary supplements?
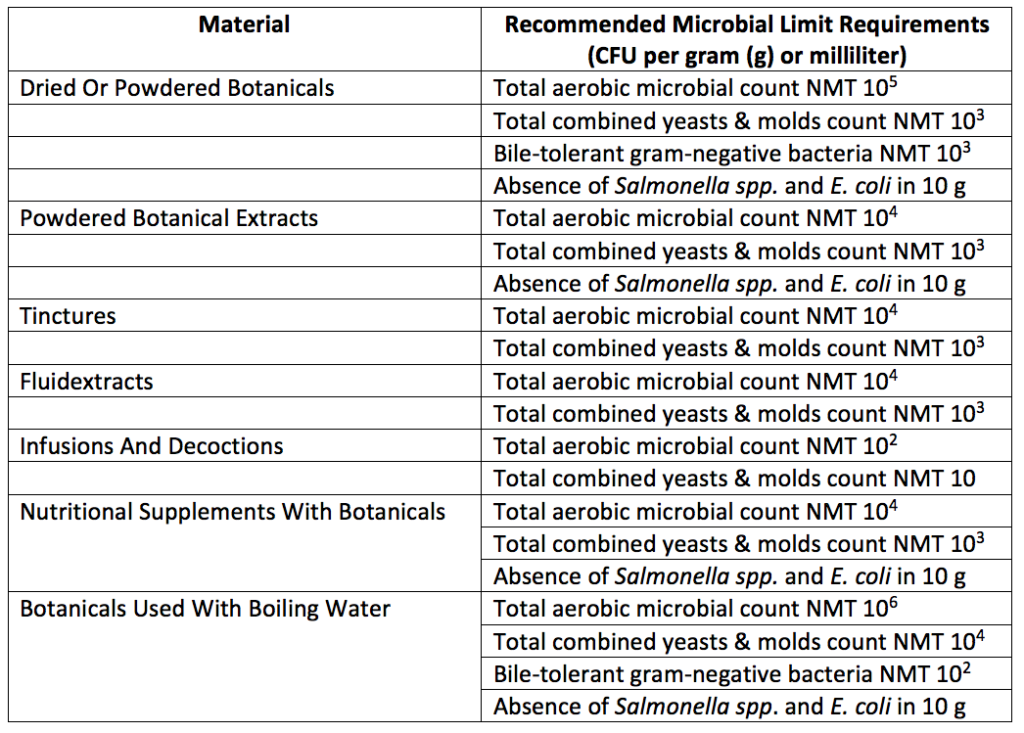
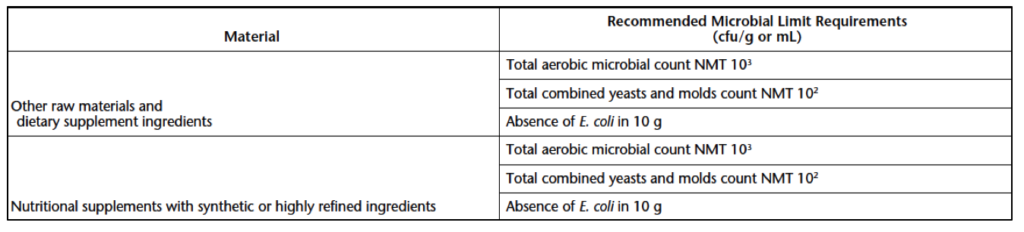
Acceptable limits for microbial levels of raw materials, excipients, and botanical products are given in Table 2. Microbial requirements for raw materials, excipients, active ingredients, and other non-sterile finished articles that do not contain botanicals are detailed in Table 3 below. In addition to the requirements below, dietary supplements containing botanicals with a history of mycotoxin contamination must undergo aflatoxin testing. Requirements for aflatoxin testing can be found in USP 561.
Summary
Overall, dietary supplements, cosmetics, and medical products and are manufactured using aseptic and non-sterile processes. Non-sterile processes monitor microbial levels within the manufacturing facility but do not have as stringent requirements as aseptic processes (which aim to eliminate any microbial ingress). Environmental monitoring of facilities, equipment, water sources, and raw material sources for non-sterile processes ensures that acceptable microbial levels for manufactured products are met. Microbial enumeration testing of dietary supplements and their environments quantifies bacterial, yeast, and mold levels for products. Acceptable limits for various bacteria, yeasts, and molds within dietary supplements are detailed in this article. All in all, make sure you choose a contract testing organization that can support you with appropriate microbiology testing for your dietary supplement or cosmetic product.
MycoScience is a contract manufacturing organization specializing in sterile syringe and vial filling. MycoScience also offers Preservative Efficacy Testing, Sterilization Validations, Bioburden Testing, Cleaning Validations, Microbial Aerosol Challenge Testing, Accelerated Aging, Microbiology Testing, Cytotoxicity Testing, Bacterial Endotoxin Testing, EO Residual Testing, Package Integrity Testing & Environmental Monitoring services medical devices and allied industries. MycoScience is an ISO 13485 certified facility.
References
U.S. Food & Drug Administration. What You Need to Know About Dietary Supplements. 2017.
United States Pharmacopeial Convention. <1115> Bioburden Control of Non-Sterile Drug Substances and Products. Rockville, MD, USA. 2021. (USPC <1115>).
United States Pharmacopeial Convention. <2023> Microbiological Attributes Of Nonsterile Nutritional And Dietary Supplements. Rockville, MD, USA. 2021. (USPC <2023>).
Sharing this in your social netwroks

