Why Sterile Fill-finish Processes Are Rising In Popularity
Injectable pharmaceuticals, IV drugs, and prefilled syringe products, commonly referred to as parenteral drug products or parenteral drugs, have been rising in popularity over oral formulations. One of the reasons for the rapid increase in injectables over pills or tablets is that injectable drug administration has a higher bioavailability for the administered active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), where API is the part of the drug formulation that has a therapeutic effect on the body. Higher bioavailability of the API means that less drug is required to have a therapeutic effect for a patient. Less patient drug administration results in a lower risk of side effects and side effect severity for patients. Less API also decreases production costs of the drug per treatment. Thus, there are both physiological and monetary benefits to parenteral drugs regarding bioavailability. The sterility requirements for injectable drug formulations require sterile fill-finish processes. There are two types of sterile fill finish operations. One process is an aseptic fill that follows all FDA-regulated guidelines for aseptic processes. All parts of the final product are separately sterilized and filled under aseptic conditions for aseptic fillings. Thus, no terminal sterilization step is required after the filling, stoppering, and sealing processes for aseptic fillings. The second process is non-aseptic filling. For non-aseptic fillings, FDA regulations for aseptic processes are not followed. Thus, a terminal sterilization step for non-aseptic fillings will be required after the product is filled, stoppered, and sealed before patient use. It is expected that the contract manufacturing industry will continue to grow in the areas of fill-finish and lyophilization to support the rising parenteral drug product manufacturing. Below we describe three primary factors linked to the rise in popularity of sterile fill finish for biologics and other products. Based on the introduction above, the first factor will come as no surprise, but the statistics might.
Factor #1: Rise of injectable pharmaceuticals
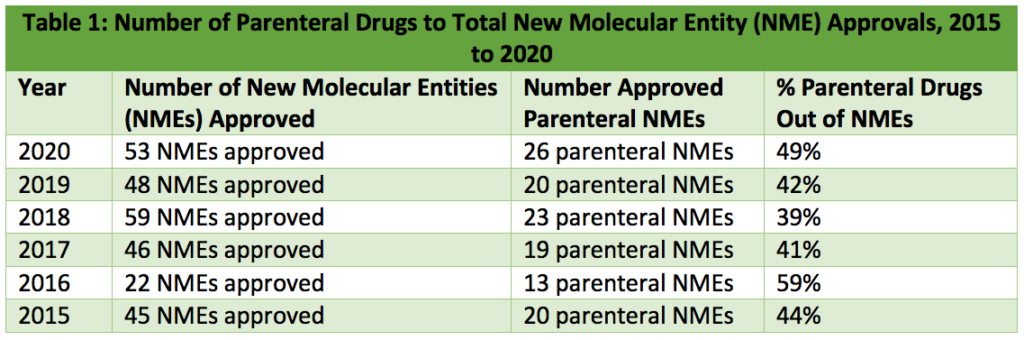
Of the forty-eight new molecular entities (NMEs) approved by the FDA in 2019, twenty were parenteral drugs, representing 42% of NME approvals [1]. In 2020, injectables accounted for 49% of NME approvals, with twenty-six out of fifty-three FDA approved NMEs being injectables [2]. Table 1 below compares FDA parenteral NME approvals from 2015-2020.
Factor #2: Rise in rare disease treatments
Many pharmaceutical companies have shifted their focus from developing blockbuster drugs to creating treatments for rare diseases, also known as orphan drugs. This shift is primarily due to Federal incentives from the Orphan Drug Act (ODA) enacted in 1983, which provides incentives to companies that pursue rare disease treatments [3]. Often these rare disease treatments require parenteral drug formulations. With the ODA supporting the private sector’s development of drugs that treat rare diseases, hundreds of new rare disease treatments have been created. However, the rare disease market is still an unmet need, with one in ten Americans suffering from one of over seven thousand different rare diseases [3,4]. Due to the OAD, the global orphan drug market is estimated to reach $209 billion by 2022 in the United States [5].
Factor #3: Rise in prefilled syringe usage
Recently, there has been an increase in prefilled syringe usage in healthcare. Prefilled syringes have risen in popularity as they minimize contamination risk, are easy to administer to patients, and consistently deliver accurate dosages [6]. With these advantages, prefilled syringes are likely to continue to rise in popularity along with the expanding global parenteral drugs market. Anticipate seeing an increase in sterile fill finish for biologics in prefilled syringes and other injectable forms.
Summary
Despite the manufacture of parenteral drugs being more complex than oral drugs, nearly half of all new molecular entities approved by the FDA every year are parenteral drug products. The rise of injectable pharmaceuticals, the increase in rare disease treatment development, and the increase in prefilled syringe usage for sterile fill finish biologics contribute to increasing popularity and need for sterile fill finish operations. As the demand for sterile fill finish operations rises, it will be necessary for pharmaceutical companies to partner with a contract manufacturer that can support the fill-finish production needs of their unique parenteral product.
MycoScience is a contract manufacturing organization specializing in sterile syringe and vial filling. MycoScience also offers Preservative Efficacy Testing, Sterilization Validations, Bioburden Testing, Cleaning Validations, Microbial Aerosol Challenge Testing, Accelerated Aging, Microbiology Testing, Cytotoxicity Testing, Bacterial Endotoxin Testing, EO Residual Testing, Package Integrity Testing & Environmental Monitoring services medical devices and allied industries. MycoScience is an ISO 13485 certified facility.
References
Patricia Van Arnum. Tracking Parenteral Drugs in New Drug Approvals. DCAT Value Chain Insights. February 2020.
Food And Drug Administration. Novel Drug Approvals For 2020. January 2021.
PhRMA. Progress In Fighting Rare Diseases.
Tim Wright. Parenteral Drug Trends. Contract Pharma. March 2020.
Kavisha Jayasundara et al. Estimating the clinical cost of drug development for orphan versus non-orphan drugs. Orphaned Journal of Rare Diseases. January 2019.
Sharing this in your social netwroks

