What is the Magnusson & Kligman Test For Sensitization?
What is sensitization testing?
Sensitization tests are tests in live animals that evaluate the ability of leachables and unknown antigens to cause hypersensitivity. The tests are designed to determine if a patient will develop a reaction with repeated exposure to a medical device. A few important factors to consider when selecting a sensitivity test include the type and extent of contact with the body, the chemical composition of the product or materials, the product’s manufacturing process, and the product’s sterilization process. Skin sensitization test on animals, drug sensitization, and contact sensitization testing will be covered in this article related to Magnusson & Kligman guinea pig maximization sensitization testing.
What is needed for sensitization testing?
Skin sensitization testing in animals will require a certified animal care facility, trained technicians, animals, and an injectable formulation of the cosmetic, drug, or device extract undergoing testing. Most companies that provide animal skin sensitization testing services will be able to cover all facility, animal, staffing, and documentation needs for sensitivities testing. However, obtaining and filling an injectable formulation for your cosmetic, drug, or medical device extracts will require additional outsourcing. Companies, like MycoScience, can support cost-effective syringe filling and vial filling for sensitization testing (such as drug contact sensitization testing) and other regulatory tests in animals.
What tests are used for sensitization testing?
Table 1 summarizes the top nine methods used for regulatory sensitization testing. Drug contact and plastic sensitivity evaluations mainly utilize guinea pigs. The Magnusson & Kligman Guinea Pig Maximization Test (GPMT) is the gold standard for sensitization testing. All other tests are alternatives to the GPMT gold standard. Some sensitization tests evaluate implanted solid articles, while others only evaluate extracts of solid articles. In some medical device and implant applications, toxicology requirements may be satisfied with data available from previously marketed products.

How is the Magnusson & Kligman guinea pig maximization test (GPMT) performed?
The Magnusson & Kligman sensitization test has three primary phases: intradermal injection, topical application, and challenge phase. All three phases are used to evaluate plastic and drug contact sensitization.
Animal Care & Preparation
Albino guinea pigs that are all male, all female, or mixed-sex are used for the GPMT. Before sensitization testing, all animals should be healthy and weigh between 300-500 grams. At least ten test animals and five control animals are used for each study. Twenty test animals and ten control animals are often needed to detect weak sensitizers accurately. For plastic and drug contact sensitization testing, animals are randomly selected into control or test groups. Animals are also clipped or shaved around the intrascapular region.
Sample Concentration Determination
Product formulations and materials are injected intradermally for Magnusson & Kligman sensitization testing. Extracts of solid materials for skin contact sensitization testing can be made using the guidelines in USP 88. Two or three additional animals are used to determine the concentration of the product injected for sensitization studies. For concentration determination, 0.1 milliliters of various concentrations of the product or product extracts are injected and examined for redness after 24-hours. The concentration that causes mild to moderate irritation (e.g., no severe skin destruction or systemic toxicity) should be used for intradermal injections and topical applications. Use the highest concentration of test article or extract that does not cause redness for the challenge phase of the GPMT.
Intradermal Injection Phase
For this phase, three pairs of intradermal injections (0.1 milliliters each) are administered into the intrascapular region of test and control guinea pigs. Injection pairs are administered on opposite sides. Injection pairs 1 and 2 are injected closer to the head of the animal, whereas injection pair 3 is administered towards the tail.
Injection pair 1: Test animals receive a 1:1 mixture of Freund’s Complete Adjuvant (FCA) and an appropriate solvent or diluent (see USP 88 In-Vivo Cytotoxicity). Control animals receive a 1:1 mixture of FCA and saline.
Injection pair 2: Test animals receive the concentration of product determined in the “Sample Concentration Determination” section above, along with an appropriate solvent or diluent. Control animals receive only the solvent or diluent.
Injection pair 3: Test animals receive a 1:1 mixture of FCA and the concentration of product determined in the “Sample Concentration Determination” section. Control animals receive a 1:1 mixture of FCA and solvent or vehicle.

Topical Application Phase
Seven days after the intradermal injection phase, apply a topical to the intrascapular region of each animal. Test animals should have pieces of filter paper or absorbent gauze loaded with the concentration of product determined in the “Sample Concentration Determination” section applied to each intradermal injection site. Control animals receive pieces of filter paper or absorbent gauze loaded with an appropriate solvent or diluent is instead of product extract. Remove the dressings and patches 48-hours after application.
Challenge Phase
The challenge phase occurs fourteen days after the topical application phase. For the challenge, filter paper patches or chambers are soaked with test article extracts in the concentration specified in the “Sample Concentration Determination” section. The patches or chambers are secured with a dressing to shaved test sites (on control and test animals). Then the patches or chambers are removed after 24-hours of exposure.
Data Results & Interpretation
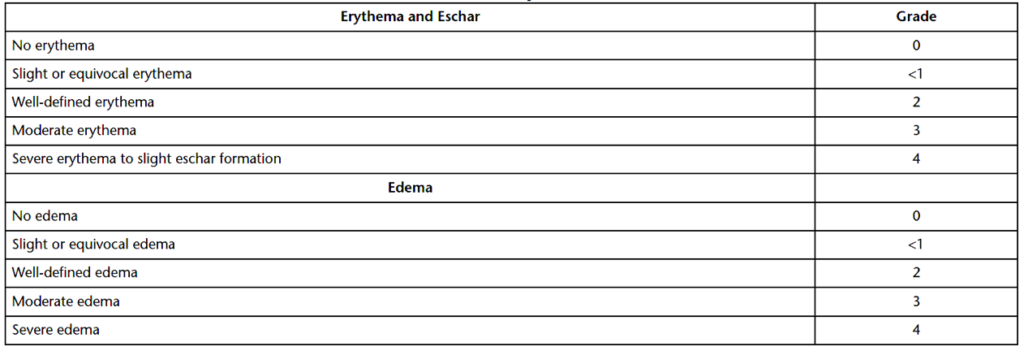
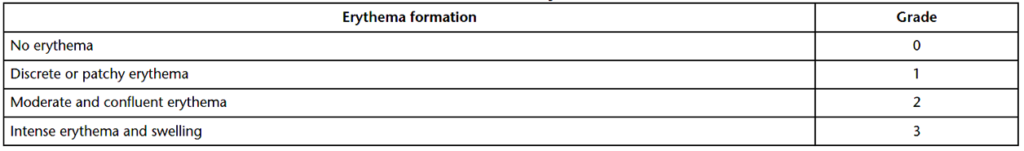
At 24-hours, 48-hours, and 72-hours after challenge patch removal, test sites on control and test animals are assessed for sensitization. All signs of reactivity should be recorded, especially any redness or swelling (edema). True edema will whiten under gentle pressure. The longer the period of whitening, the greater the edema. Sensitivity tests can be evaluated in three ways: percentage of responsive test animals (Table 2), erythema & edema (Table 3), and erythema only (Table 4). Note that for Table 1, GPMTs with ten test animals will have percentiles of 0, <10%, 10%–30%, 31%–60%, 61%–80%, and 81%–100. Grades of one or higher in the test animals, with controls at grades less than one, indicates product sensitization. If control animals display grade 1 reactivity and the test animals display reactivity above the controls, product sensitization is suspected. Statistical analysis (e.g., chi-square contingency table and Mann-Whitney U test) is used to determine if the differences in scores between treated and control guinea pigs are significant. Any response in the negative control group under Magnusson & Kligman Guinea Pig Maximization Testing indicates irritation potential for the product or material being tested. If irritation in controls occurs, test and control animals should be rechallenged one week later with a reduced concentration of the product extract preparation on the untreated side of the animal.

Summary
Overall, sensitization tests evaluate the ability of leachables and unknown antigens to cause hypersensitivity. The tests are designed to determine if a patient will develop a reaction with repeated exposure to a medical device or implant. All sensitivity tests are in-vivo animal studies, and most of these studies utilize guinea pigs for sensitivity evaluations. The Magnusson & Kligman Guinea Pig Maximization Test (GPMT) is the gold standard for sensitization testing. The GPMT has three primary phases: the intradermal injection phase, the topical application phase, and the challenge phase. Further, GPMTs can be evaluated in three ways: percentage of responsive test animals (Table 2), erythema & edema (Table 3), and erythema only (Table 4). All in all, ensure you choose a contract testing organization that can support you with appropriate toxicity testing for your unique medical device or product needs.
MycoScience is a contract manufacturing organization specializing in sterile syringe and vial filling cosmetic products or for products used in animal studies. In addition, MycoScience offers testing services, including Preservative Efficacy Testing, Cytotoxicity Testing, Bioburden Testing, Cleaning Validations, Microbial Aerosol Challenge Testing, Accelerated Aging, Microbiology Testing, EO Residual Testing, Bacterial Endotoxin Testing, Package Integrity Testing, Sterilization Validations & Environmental Monitoring services medical devices and allied industries. MycoScience is an ISO 13485 certified facility.
References
United States Pharmacopeial Convention. <1184> Sensitization Testing. Rockville, MD, USA. 2021. (USPC <1184>).
Sharing this in your social netwroks

